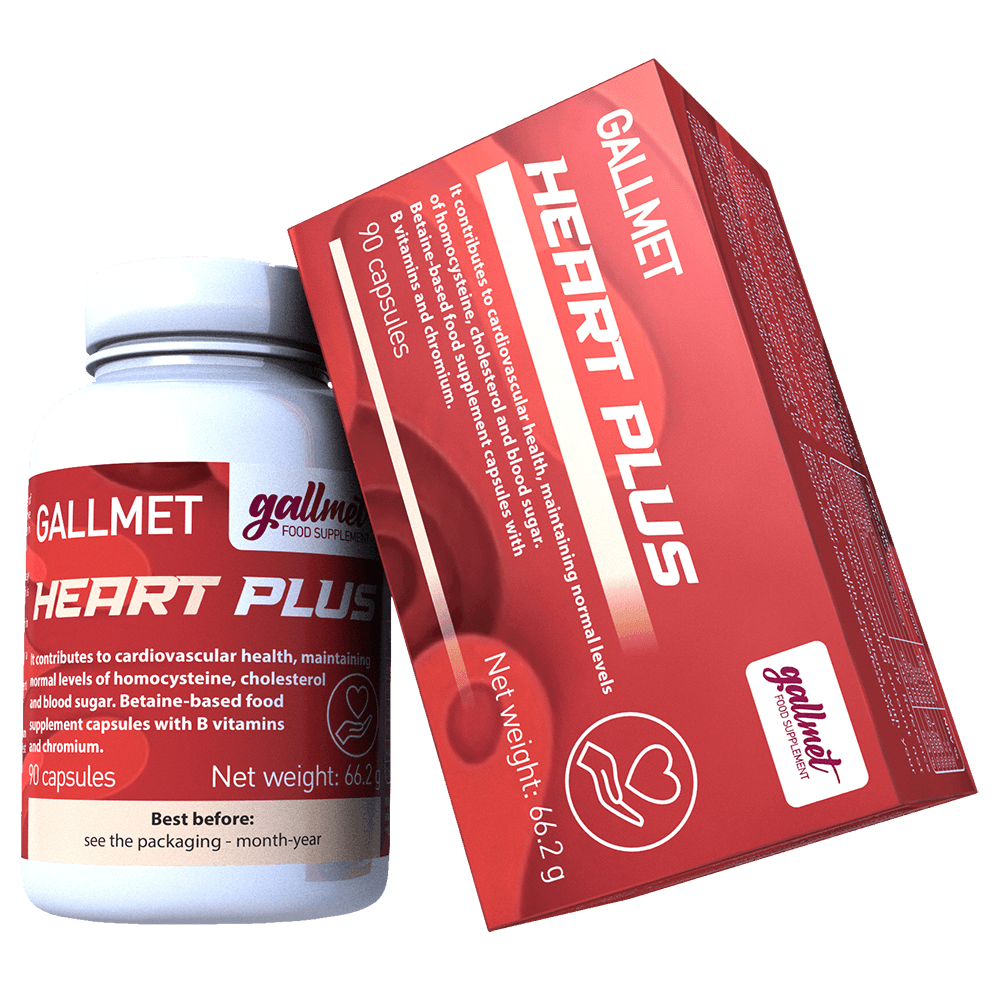
Association of gout with kidney damage (nephropathy) and homocysteine levels in the blood
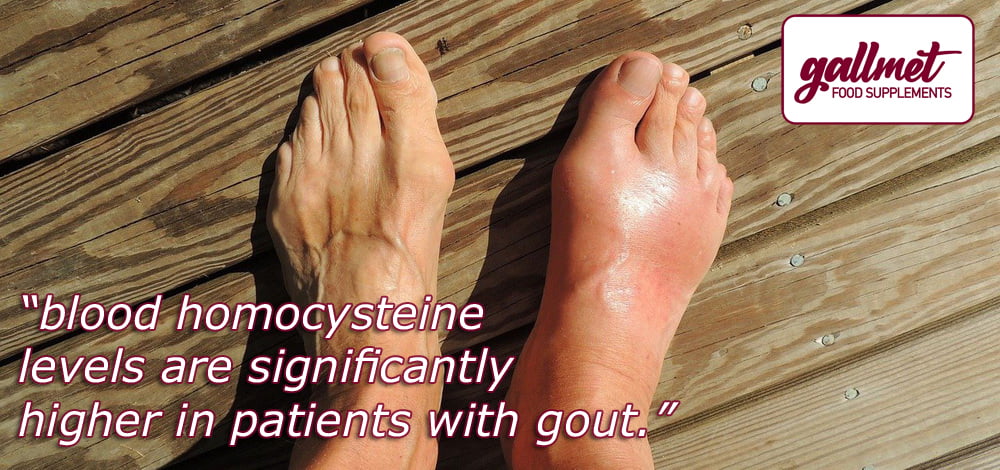
Gout (arthritis uricat) can be hereditary, but it can also be caused by diet, alcohol consumption habits, etc., as well as by improper kidney function, enzyme deficiencies, enzyme dysfunction. Blood uric acid levels are not significantly different between gouty and healthy people, but blood homocysteine levels are significantly higher in gout patients. Impaired renal function is associated with blood homocysteine levels and with the likelihood of developing and worsening gout.1 Renal failure is the most common cause of death in gout patients. High level of homocysteine cause kidney damage and thus play a role in the development of chronic renal failure.2 Laboratory eGFR is a measure of kidney function, with lower levels associated with higher homocysteine levels and a one unit increase in homocysteine is associated with more than 8 times the risk of elevated blood uric acid levels, which contributes to the development of gout.3
But what is homocysteine?
What can I do about gout?
- Avoiding alcohol,
- gout diet,
- drinking plenty of fluids (2-3 litres/day):
- non-carbonated water,
- medicinal waters (e.g. Balfi, Parádi, Salvus),
- nettle tea.
- Vitamin C and D supplementation,
- calcium supplementation,
- reducing homocysteine levels.
GALLMET Heart Plus capsules contain folate (vitamin B9), betaine, vitamins B6 and B12, which contribute to the body's proper homocysteine levels!💊
What ingredients are effective against gout?
People with high homocysteine levels have higher blood levels of uric acid and lower levels of folate (vitamin B9) and vitamin B12 than healthy people. Vitamin B9 (folate) and vitamin B12 may be useful for high uric acid and homocysteine levels in vascular disorders such as kidney damage.5
Folate reduces uric acid levels to a greater extent the higher the homocysteine level. 6 The folate intake of people in central Europe is also very low at only about a third of the level recommended in dietary recommendations.7 In addition to this, many of the foods that are forbidden or avoided in the gout diet are also the main source of vitamin B12, so vitamin B12 deficiency can be exacerbated.
It should be noted that many products containing vitamin B9 contain folic acid, while the bioavailability of folic acid is not the same as natural folate in patients with common gene defects - MTHFR 1298C and C677T. Folic acid does not directly reduce homocysteine levels but can cause kidney damage and, unlike natural folate, does not cross the blood-brain barrier!8
How do I know for sure that I have inherited the MTHFR C677T gene defect?
- Laboratory tests: Synlab
A betaine-rich diet may be effective in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.9 Supplementation with betaine is most important in patients who do not respond to vitamin B6 supplementation and in those who do not follow a low protein and low methionine diet.10
TRY GALLMET HEART PLUS CAPSULES NOW AT A SPECIAL INTRODUCTORY PRICE!
Click on the [print-me] icon to print the page
[1] Elevated Serum Homocysteine Levels Were Not Correlated with Serum Uric Acid Levels, but with Decreased Renal Function in Gouty Patients - Sang Tae Choi, Jin Su Kim and Jung-Soo Song https://www.researchgate.net/publication/263130600_Elevated_Serum_Homocysteine_Levels_Were_Not_Correlated_with_Serum_Uric_Acid_Levels_but_with_Decreased_Renal_Function_in_Gouty_Patients
[2] Homocysteine in Renal Injury - Yanjun Longa and Jing Niea https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4947689/
[3] Serum Homocysteine Level Is Positively Correlated With Serum Uric Acid Level in U.S. Adolescents: A Cross Sectional Study - Yumeng Shi, Zuxiang Wu, Ji Wu, Zhiqiang Chen and Ping Li https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.818836/full
[4] Homocysteine - from disease biomarker to disease prevention - Smith AD, Refsum H. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/joim.13279
[5] The Different Relationship between Homocysteine and Uric Acid Levels with Respect to the MTHFR C677T Polymorphism According to Gender in Patients with Cognitive Impairment - Hee-Jin Kim, Il Woong Sohn, Young Seo Kim and Jae-Bum Jun https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/4/1147/htm
[6] Folic acid therapy reduces serum uric acid in hypertensive patients: a substudy of the China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial (CSPPT) - Xianhui Qin, Youbao Li, Mingli He, Genfu Tang, Delu Yin, Min Liang, Binyan Wang, Jing Nie, Yong Huo, Xin Xu and Fan Fan Hou https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/105/4/882/4638049
[7] The role of homocysteine in the pathogenesis of early-onset ischaemic heart disease - Dr. Lajos Szollár http://real.mtak.hu/62/1/34815_ZJ1.pdf
[8] New Evidence for Homocysteine Lowering for Management of Treatment-Resistant Hypertension - Merrill F. Elias and Craig J. Brown https://academic.oup.com/ajh/article/35/4/303/6475983
[9] Human Nutrition and Metabolism Research Communication - Margreet R. Olthof, Trinette van Vliet, Esther Boelsma and Petra Verhoef https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/133/12/4135/4687457
[10] Health Functionalities of Betaine in Patients With Homocystinuria - Truitt C, Hoff WD, Deole R. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8459993/
All health recommendations related to homocysteine level

Homocysteine
About homocysteine - a little biochemistry and history
Circulatory disorders
Association of cardiovascular diseases with homocysteine levels
Diabetes
Association between diabetes and blood homocysteine levels
Metabolic syndrome
Association between metabolic syndrome and homocysteine levels
Gout
Association of gout with kidney damage and homocysteine levels in the blood

Neuro-degenerative diseases
In case of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and dementia

Coronavirus infection
Association between severe coronavirus infection and high homocysteine levels
Cancer
Association of cancer with insufficient vitamin B9 utilisation

Folic acid or folate
Folic acid or folate - what's the difference?